You are given n distinct points on a plane with integral coordinates. For each point you can either draw a vertical line through it, draw a horizontal line through it, or do nothing.
You consider several coinciding straight lines as a single one. How many distinct pictures you can get? Print the answer modulo 109 + 7.
The first line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of points.
n lines follow. The (i + 1)-th of these lines contains two integers xi, yi ( - 109 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 109) — coordinates of the i-th point.
It is guaranteed that all points are distinct.
Print the number of possible distinct pictures modulo 109 + 7.
4 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 2
16
2 -1 -1 0 1
9
In the first example there are two vertical and two horizontal lines passing through the points. You can get pictures with any subset of these lines. For example, you can get the picture containing all four lines in two ways (each segment represents a line containing it).
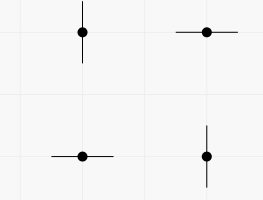 The second way:
The second way: 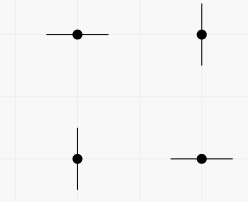
In the second example you can work with two points independently. The number of pictures is 32 = 9.
题意:
给出二维平面上的n个点,每个点可以画一条水平线,也可以画一条竖直线,也可以什么都不画
求 图案 方案数
思路:把冲突的点放到一个连通块中,对每个连通块单独处理,乘法原理计数
对于一个连通块来说,n个点最多有n+1条边
最开始一个点有2条边,然后每加入一条边,都要加入一个点
当然,可以只加点不加边(例:井字形)
所以 边数E<=点数P+1
因为连通块里加入的这些边,保证不冲突
所以
1、E==P+1
因为一个点只能连一条边,所以这个连通块最多只能有P条边
所以这个连通块的方案数=C(E,1)+C(E,2)+……+ C(E,P)= 2^E-1
2、E<=P
方案数=C(E,1)+C(E,2)+……+C(E,E)= 2^E
#include#include #include #define N 100001using namespace std;const int mod=1e9+7;int hasx[N],hasy[N],x[N],y[N];int fa[N*2];int sizp[N],size[N*2];void read(int &x){ x=0; int f=1; char c=getchar(); while(!isdigit(c)) { if(c=='-') f=-1; c=getchar(); } while(isdigit(c)) { x=x*10+c-'0'; c=getchar(); } x*=f;}int find(int i) { return fa[i]==i ? i : fa[i]=find(fa[i]); }int Pow(int a,int b){ int res=1; for(;b;a=1ll*a*a%mod,b>>=1) if(b&1) res=1ll*res*a%mod; return res;}int main(){ int n; read(n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) read(x[i]),read(y[i]),hasx[i]=x[i],hasy[i]=y[i]; sort(hasx+1,hasx+n+1); sort(hasy+1,hasy+n+1); int tot1=unique(hasx+1,hasx+n+1)-hasx-1,cnt=tot1; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) x[i]=lower_bound(hasx+1,hasx+tot1+1,x[i])-hasx; int tot2=unique(hasy+1,hasy+n+1)-hasy-1; cnt+=tot2; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) y[i]=lower_bound(hasy+1,hasy+tot2+1,y[i])-hasy; for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) fa[i]=i; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) fa[find(x[i])]=find(y[i]+tot1); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) sizp[find(x[i])]++; for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) size[find(i)]++; int ans=1; for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) if(find(i)==i) { if(sizp[i]+1==size[i]) ans=1ll*ans*(Pow(2,size[i])+mod-1)%mod; else ans=1ll*ans*Pow(2,size[i])%mod; } printf("%d",ans);}